Prion Disease Treatment: Breakthrough Gene-Editing Therapy
Prion disease treatment has long been a topic of interest in the medical community, particularly due to the devastating and invariably fatal nature of these disorders. Conditions such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia highlight the urgent need for effective therapies, particularly as prion diseases stem from misfolded proteins in the brain. Recent advancements in prion disease research offer a glimmer of hope, especially a promising gene-editing therapy that has shown success in laboratory mice. Employing revolutionary techniques like base editing, researchers have discovered they can significantly reduce harmful protein levels, thereby extending lifespans. As the field progresses toward human trials, the collaboration between dedicated patient-scientists and experts promises to push the boundaries of treatment for these notoriously challenging conditions.
Exploring treatment options for prion diseases, also referred to as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, reveals a growing interest in innovative therapies. These disorders are characterized by the accumulation of abnormal proteins, leading to severe neurological deficits and ultimately death. The emergence of advanced methodologies, including a novel base editing technique, signifies a transformative approach in combating conditions like Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease and fatal familial insomnia. With ongoing prion disease research yielding encouraging results, the ultimate goal remains the development of effective clinical interventions. Such advancements underscore the importance of integrating patient experiences with scientific inquiry, paving the way for new hope in the realm of neurodegenerative diseases.
Understanding Prion Diseases and Their Impact
Prion diseases are a group of rare yet devastating neurological disorders that have garnered significant attention in recent years. These diseases, caused by misfolded prion proteins in the brain, lead to severe deterioration of cognitive functions, ultimately resulting in dementia and death. Among the most recognized variants are Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, fatal familial insomnia, and Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease. The nature of these disorders is particularly alarming as they are invariably fatal, often progressing rapidly, and presenting numerous challenges for treatment and patient care.
The societal impact of prion diseases extends beyond the medical realm, influencing families and communities profoundly. For many affected, the diagnosis can feel like a death sentence, not just for themselves but for their loved ones who might also be at risk due to hereditary forms of the disease. As prion diseases can arise from both genetic mutations and sporadic occurrences, the uncertainty surrounding their origins adds to the emotional burden on patients and families alike.
Advancements in Prion Disease Treatment
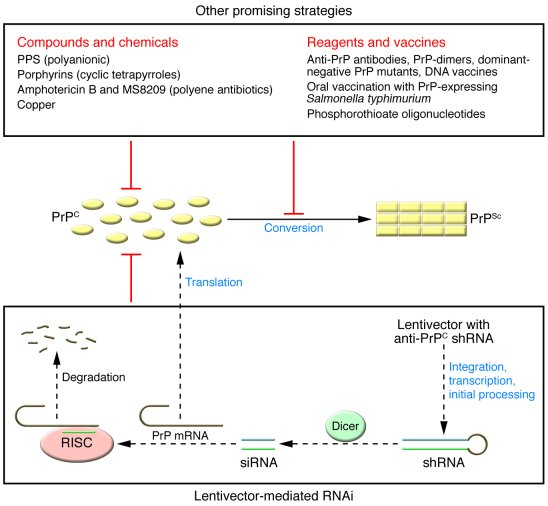
Recent advancements in the treatment of prion disease have generated a beacon of hope for patients and their families. A pivotal study conducted at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard has demonstrated the potential of a novel gene-editing therapy, utilizing a base editing technique to amend the genetic anomalies responsible for prion protein misfolding. By successfully altering a single base in the gene that encodes the harmful proteins, researchers were able to reduce protein levels in the brains of laboratory mice significantly, extending their life spans by over 50%. This promising development could pave the way for future treatments aimed directly at the root causes of prion diseases.
Despite the encouraging findings, researchers remain cautious. The transition from experimental results in animal models to human clinical trials is fraught with challenges. There are stringent regulatory pathways and safety protocols that must be adhered to before any new treatment can reach patients. Researchers are actively working to refine the gene-editing techniques to enhance efficacy and safety, which is essential given the potential complications associated with prion diseases, including the risks of prion transmission.
The Role of Patient-Scientists in Prion Disease Research
The involvement of patient-scientists in prion disease research adds a deeply personal dimension to the scientific endeavor. Scientists like Sonia Vallabh, who is battling fatal familial insomnia, bring not only their expertise but also their lived experiences into the lab. This unique perspective fuels a commitment to finding meaningful solutions for a disease that has touched their lives and the lives of their families. Vallabh’s work at the Broad Institute, alongside her spouse Eric Minikel, exemplifies the powerful fusion of personal motivation and professional scientific inquiry.
Their journey from diagnosis to scientific inquiry underlines an inspiring narrative of resilience and dedication. Vallabh and Minikel’s connection to the disease emphasizes the importance of empathy in medical research, reminding fellow researchers and the public that behind every scientific study, there are real lives and personal stakes. This collaboration between patient-scientists and established researchers is crucial for driving forward innovative therapies and translating laboratory discoveries into viable treatments for prion diseases.
The Future of Gene-Editing Therapies in Treating Prion Disorders
As the field of gene-editing therapy evolves, the potential for treating prion disorders is becoming increasingly tangible. Techniques like base editing not only hold promise for prion diseases but could also revolutionize the treatment landscape for various genetic disorders. Researchers are focusing on improving the precision and safety of these editing methods, particularly in the context of infectious agents such as prions, which pose unique challenges due to their resilient nature.
Looking ahead, multidisciplinary collaboration will be key to advancing research and transitioning findings from the lab to clinical settings. As scientists refine these gene-editing techniques and develop new therapies, ongoing discussions about ethical considerations and safety protocols will be paramount. This commitment to responsible innovation must be upheld to ensure that the benefits of these medical breakthroughs can be safely realized for future patients suffering from prion diseases.
Challenges in Conducting Prion Disease Research
Conducting research on prion diseases comes with a set of challenges that must be navigated with caution. One of the primary hurdles lies in the safety concerns associated with prions, which are notoriously difficult to handle due to their ability to cause severe neurodegenerative diseases. Historical incidents, such as laboratory accidents that resulted in the transmission of prion diseases to researchers, underscore the importance of stringent safety protocols in experimental settings.
Additionally, the inherently slow progression of clinical research in prion diseases, combined with the necessity for animal models to evaluate therapeutic efficacy, complicates the research timeline. Establishing the relevant biomarkers for these disorders is another critical area of focus that scientists must address before proceeding to human clinical trials. Striking a balance between rapid innovation and careful, methodical research processes will be vital for overcoming these obstacles.
The Importance of Collaborative Research Efforts
Collaboration is at the heart of effective scientific research, particularly in fields as complex as prion disease studies. The interdisciplinary nature of this research often brings together geneticists, neurologists, and patient advocates, all contributing varied expertise to tackle the multifaceted challenges associated with prion diseases. The collaboration between labs, such as those at the Broad Institute and Harvard Medical School, fosters an environment of shared knowledge and resources, accelerating the pace of discovery.
Such collaborative efforts are particularly critical in prion disease research, where collective knowledge can lead to innovative solutions that might not be possible in isolation. Engaging patient-scientists alongside traditional researchers allows for a deeper understanding of patient needs and enhances the motivation within research teams. This synergy between diverse fields of study exemplifies how collaborative research can lead to breakthroughs that have the potential to change the trajectory of prion disease treatment.
Ethical Considerations in Prion Disease Studies
As with any emerging medical treatment, ethical considerations play a crucial role in prion disease research. The potential for gene-editing therapies to alter genetic material invokes significant ethical discussions regarding consent, privacy, and the implications of genetic modifications. Researchers must navigate these multifaceted concerns, ensuring that their approaches are not only scientifically sound but also aligned with ethical standards and patient rights.
Moreover, the unique nature of prion diseases raises additional ethical concerns surrounding the risks associated with patient recruitment for clinical trials, especially given the possibility of adverse outcomes. Adequate measures must be established to inform participants of potential risks and benefits associated with new therapies. Ensuring transparent communication and informed consent processes will be essential in maintaining public trust and advancing clinical research effectively.
The Role of Government and Research Institutions in Prion Disease Funding
Government and private institutions play a pivotal role in driving forward research on prion diseases by providing essential funding and resources. Funding bodies, such as the National Institutes of Health, support groundbreaking studies that focus on innovative treatment options and basic scientific understanding of prion diseases. Such financial backing allows researchers to pursue ambitious projects that could lead to significant advancements in treatment and patient care.
Moreover, increased investment in prion disease research reflects a commitment to addressing rare diseases that often lack adequate attention and resources. This funding not only facilitates laboratory research but also enhances collaborations that span multiple disciplines, helping to bridge gaps between basic research and clinical application. By fostering a supportive funding environment, we ensure that researchers can continue their vital work towards finding effective therapies for those impacted by prion diseases.
Empowering Patient Communities in Prion Disease Research
Empowering patient communities is a critical aspect of advancing research in prion diseases. Engaging those affected by these disorders and their families can help inform research priorities and provide essential insights into the real-world impact of these diseases. Patient advocacy groups play an instrumental role in raising awareness, promoting funding for research, and connecting researchers with affected individuals who can share their experiences.
Such engagement can foster a sense of shared purpose between researchers and patients, leading to more focused research efforts that truly address the needs of those impacted by prion diseases. Additionally, involving patients in the research process reinforces the principle that scientific inquiry should be patient-centered, ensuring that the outcomes of such research ultimately lead to meaningful advancements in treatment and quality of life for affected individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the latest advancement in prion disease treatment using gene-editing therapy?
Recent studies have shown that gene-editing therapy, particularly using a base editing technique, can significantly reduce harmful prion protein levels in laboratory mice’s brains. This advancement was published in Nature Medicine, highlighting how altering a single genetic base led to a 52% extension in mouse lifespan. While promising, further research and human trials are yet to follow.
How does gene-editing therapy relate to specific prion diseases like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia?
Gene-editing therapy has potential implications for treating various prion diseases, including Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia. By targeting the genetic factors causing these conditions, scientists aim to develop therapies that can effectively reduce harmful proteins associated with these disorders, ultimately aiming to improve patient outcomes.
What role has research played in understanding and treating fatal familial insomnia?
Research into fatal familial insomnia is vital, as it is a hereditary prion disease that can significantly impact individuals and families. Foundational studies, such as those led by patient-scientists like Sonia Vallabh, have focused on gene-editing therapies to alter the prion protein gene responsible for the disease, showcasing advances toward a potential treatment.
What challenges lie ahead for prion disease treatment and clinical trials?
While recent advancements in gene-editing therapy for prion diseases show promise, significant challenges remain before clinical trials can commence. These include refining the base editing technology, ensuring the safety of treatments, and confirming efficacy in human models to address the unique challenges posed by prion-related disorders.
How can base editing techniques contribute to future prion disease research?
Base editing techniques, as demonstrated in recent studies, allow for precise alterations of the genetic code responsible for prion diseases. This method enhances the research possibilities for understanding and potentially treating conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease by directly targeting the genes involved, leading to more effective therapeutic strategies.
What motivates researchers in the field of prion disease treatment?
Personal connections to prion diseases often motivate researchers, particularly those like Sonia Vallabh, who are affected by conditions such as fatal familial insomnia. The involvement of patient-scientists can drive an intense commitment to finding effective treatments and advancing research in this critical area.
What is the significance of collaboration in prion disease treatment research?
Collaboration among researchers is crucial in advancing prion disease treatment. The integration of expertise from various fields, such as gene editing and vector engineering, facilitates innovative approaches, accelerates research, and may enhance safety measures, ultimately moving toward effective therapies for these challenging disorders.
What are prion diseases, and why are they difficult to treat?
Prion diseases are a group of rare, invariably fatal disorders caused by misfolded proteins that lead to brain damage and dementia. Their complexity, coupled with the infectious nature of prions, poses significant challenges for treatment development, making advancements in technologies like gene-editing therapy critical for future interventions.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Breakthrough | Development of a gene-editing therapy targeting the production of harmful prion proteins. |
| Study Findings | Single base alteration in prion protein gene reduced protein levels by 50%, extending lifespan of mice by 52%. |
| Research Team | Includes Sonia Vallabh, Eric Minikel, and David Liu, focusing on personal relevance due to their connections with prion disease. |
| Clinical Trials Timeline | Human trials are still several years away, pending additional research and refinement of the therapy. |
| Types of Prion Diseases | Includes Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia, among others. |
| Personal Motivation | Collaboration between patient-scientists and labs highlighted, emphasizing the importance of personal experiences in research. |
Summary
Prion disease treatment has reached a pivotal point with groundbreaking research showing promise in gene-editing therapies. This innovative approach offers hope for patients suffering from these lethal disorders caused by misfolded proteins. The collaboration between scientists and affected individuals underscores the urgency of developing effective treatments. While human trials remain on the horizon, the advances made in laboratory settings pave the way for future breakthroughs in combating prion diseases.