Is Sugar Addictive? Understanding Its Impact on Health
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked intense debate among health professionals and researchers alike. While sugar may not be classified as an addictive substance in the same category as alcohol or narcotics, its effects on the brain and body can lead to compelling cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. Many individuals find themselves drawn to sugary, ultra-processed foods, which can activate pleasure centers in the brain, much like traditional addictive substances. Understanding the dynamics of sugar addiction is essential for grappling with its health effects, helping to explain the struggles many face with sugar cravings and the overwhelming ubiquity of added sugars in processed foods.
Sugar, often dubbed as an unrecognized addiction, occupies a conflicting space in our diets. While it is a vital component of fruits and vegetables, the increasing consumption of added sugars in processed snacks raises concerns about sugar dependency and the adverse health effects of sugar. Many people experience intense driving desires for sweetness, making it essential to explore alternatives to combat these cravings. The concept of sugar reliance encompasses both physical and psychological dimensions as individuals navigate their relationship with food. By examining these factors, we can better understand the broader implications of sugar on our health and well-being.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
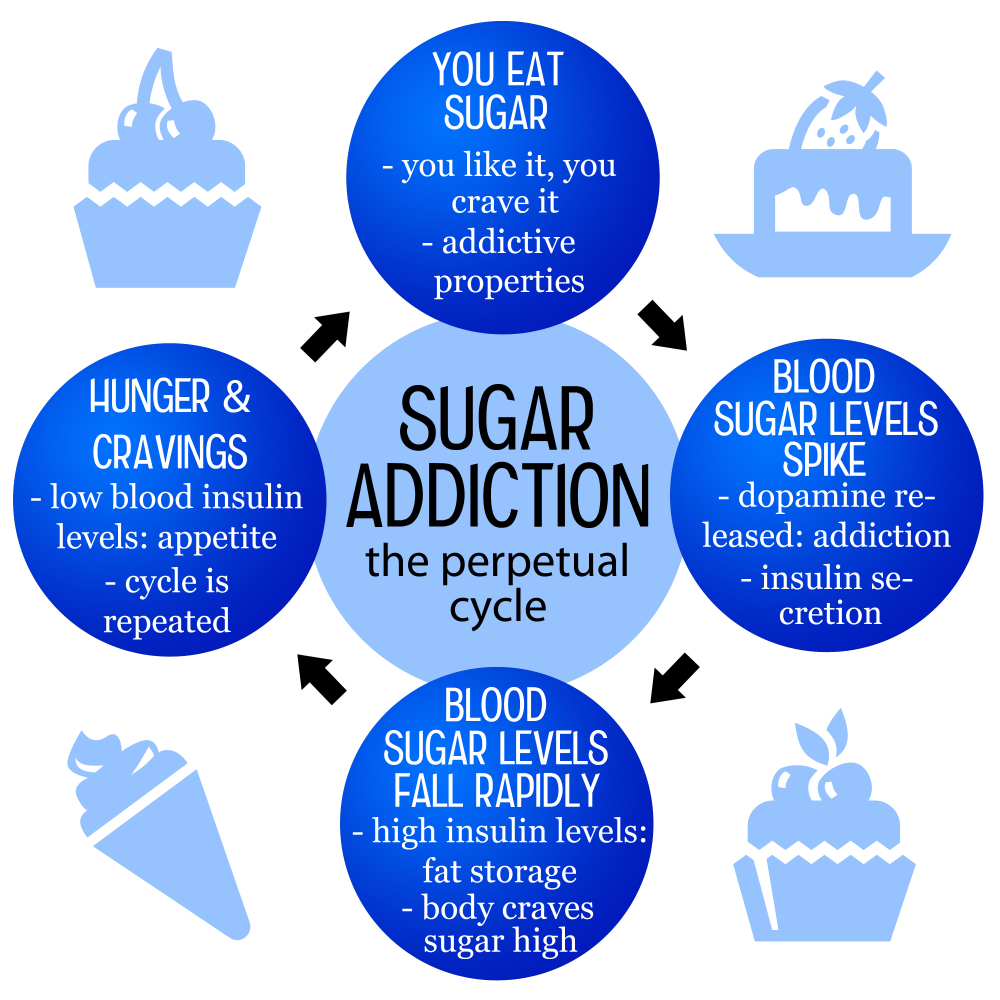
The concept of sugar addiction has been a topic of increasing interest, as studies suggest that sugar may trigger cravings similar to those associated with addictive substances such as nicotine or alcohol. While it’s not classified as an addictive substance, the compulsive eating behaviors induced by high sugar intake can feel very real for many individuals. This is particularly concerning in a society where ultra-processed foods packed with added sugars are omnipresent, creating an environment ripe for habitual overconsumption.
Additionally, the effects of sugar on brain chemistry can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms when individuals try to cut back on their intake. These symptoms may include headaches, irritability, and anxiety, highlighting the powerful impact that sugar can have on both physical and mental health. Even though sugar is a necessary carbohydrate that our bodies need, understanding its potential for addiction can help people make more informed dietary choices.
The Health Effects of Sugar on Your Body
Excessive sugar intake is linked to a myriad of health issues including obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. The American Heart Association recommends limiting sugar consumption to manage weight and reduce the risk of these chronic diseases. It is crucial to differentiate between naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and dairy products and added sugars found in processed foods, which can lead to health complications when consumed in excess.
Moreover, the gradual increase in the consumption of sugary drinks and snacks has resulted in an alarming rise in sugar-related health conditions. For instance, the average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, significantly surpassing health recommendations. This excessive intake is often correlated with negative health outcomes, underscoring the necessity for individuals to monitor their sugar consumption and make healthier food choices.
Sugar Cravings: Nature vs. Nurture
Cravings for sugary foods can stem from both biological impulses and environmental influences. On a biological level, consuming sugar activates the brain’s reward system, releasing feel-good chemicals like dopamine. This response reinforces the desire for sugar, making it more likely for individuals to seek out sweets regularly. Furthermore, habitual exposure to high-sugar processed foods can create a cycle of cravings, leading to increased desire and consumption.
On the environmental side, our modern food landscape is saturated with sugary snacks and beverages, making them easily accessible and appealing. This nexus of biology and environment explains why many find it challenging to resist sugar cravings. Strategies such as mindful eating and gradually reducing sugar intake can be effective in managing these cravings without the shock of sudden deprivation.
Processed Foods and Their Role in Sugar Consumption
Processed foods play a significant role in increasing sugar consumption in contemporary diets. Many of these foods not only contain excess added sugars but also unhealthy fats and sodium, creating a combination that is hard to resist. The convenience of grabbing a sugary snack on the go contributes to habitual consumption, further entrenching individuals in a cycle of cravings and reliance on these palatable food items.
In this scenario, awareness of food labels becomes essential. Many people are unaware of the hidden sugars present in processed foods, which can lead to exceeding daily recommended intake. By choosing whole, minimally processed foods, individuals can significantly reduce their sugar intake, promoting better health outcomes and decreasing the likelihood of developing a dependency on sugary foods.
The Psychological Impact of Reducing Sugar Intake
Reducing sugar consumption can have profound psychological effects. Many individuals report experiencing withdrawal-like symptoms when they eliminate or cut back significantly on sugar. These symptoms can include mood swings, irritability, and cravings, mirroring the psychological aspects associated with addiction to substances like nicotine. This highlights the need for a cautious approach when modifying sugar intake.
Gradually reducing added sugar rather than going cold turkey may help mitigate these psychological effects and allow for a smoother transition. Incorporating healthier alternatives that satisfy sweet cravings can also assist in adjusting one’s palate while minimizing the impact on mental well-being. Understanding these psychological nuances can empower individuals to make healthier dietary changes without feeling overwhelmed.
Sugar Intake Recommendations for Optimal Health
Health organizations recommend specific limits on sugar intake to promote overall well-being. The American Heart Association suggests keeping added sugars to a maximum of 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women per day. These guidelines are intended to help individuals maintain a balanced diet and reduce the risk of chronic diseases linked to excessive sugar consumption.
Being mindful of sugar intake and using food labels to make informed choices is essential for achieving these recommendations. Simple substitutions, like replacing sugary drinks with water or opting for fresh fruits instead of candy, can make a significant difference. By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can lead healthier lives while enjoying necessary sweetness in moderation.
The Connection Between Sugar and Mood Disorders
Research indicates a connection between high sugar consumption and mood disorders, including anxiety and depression. The rapid spikes and subsequent drops in blood sugar levels can lead to fluctuations in mood and energy, creating a roller coaster effect that can affect overall mental health. Understanding this connection can be vital for those looking to maintain emotional stability.
Moreover, reducing sugar intake has been associated with improved mood and mental clarity. By stabilizing blood sugar levels through a balanced diet rich in whole foods, individuals may experience a reduction in mood swings and an enhancement in overall emotional well-being. This illustrates the importance of dietary choices not just for physical health but for mental health as well.
Recognizing the Signs of Sugar Addiction
Identifying the signs of sugar addiction requires an honest assessment of one’s eating habits and cravings. Common indicators include persistent cravings for sugary foods, consuming sugar to cope with stress, and feeling a loss of control over sugar intake. Recognizing these signs can be the first step toward developing a healthier relationship with food.
Individuals who experience these signs may benefit from strategies such as keeping a food diary or seeking professional guidance. Often, establishing a supportive environment and seeking accountability can help individuals manage their sugar habits and reduce dependence. By taking proactive measures, one can address sugar cravings effectively, fostering a healthier lifestyle.
The Importance of Balanced Nutrition
A balanced diet is crucial for maintaining optimal health and managing sugar intake. Including a variety of nutrients, such as proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates, can reduce sugar cravings and promote satiety. Whole foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins play a vital role in nutrition and can help ward off excessive sugar cravings.
Implementing a balanced approach to nutrition can empower individuals to enjoy smaller amounts of sugar without negative health repercussions. Making informed food choices not only supports physical health but also contributes to emotional stability, creating a holistic sense of well-being. Prioritizing balanced nutrition is an effective way to combat the negative effects of sugar while maintaining enjoyment in one’s diet.
Strategies for Reducing Sugar in Your Diet
Implementing effective strategies for reducing sugar can lead to significant health improvements. Start by gradually replacing sugary snacks and beverages with healthier options, such as fruits or unsweetened yogurt. Preparing meals at home allows for greater control over ingredients and can naturally lower sugar consumption, enabling individuals to make healthier dietary choices.
Additionally, being mindful of hidden sugars in packaged foods is essential. Reading food labels can help identify added sugars that may otherwise go unnoticed. Having a proactive approach to sugar consumption can yield positive outcomes, fostering a healthier lifestyle and reducing dependence on sugary foods.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like other substances?
Sugar does exhibit some addictive qualities, as it can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. However, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol, nicotine, or opiates based on clinical criteria. The effects of sugar can resemble those of addiction, particularly with ultra-processed foods containing high amounts of added sugar, which make them more palatable and lead to habitual consumption.
What are the health effects of sugar consumption?
Excessive sugar consumption is linked to various health effects, including obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes. The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, far exceeding the recommended limits. While moderate sugar intake is acceptable, being mindful of sugar in processed foods is crucial for maintaining health.
What causes sugar cravings and how to manage them?
Sugar cravings can stem from the addictive qualities of sugar-laden processed foods, which enhance flavor and increase cravings due to their high palatability. To manage sugar cravings, experts recommend gradually reducing added sugar intake rather than going cold turkey, which can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms. Tracking food labels and being aware of sugar consumption can also help.
How does sugar addiction differ from substance addiction?
Unlike alcohol or drugs, sugar is a nutrient necessary for survival and is present in many healthy foods such as fruits and dairy. While sugar can create cravings and habitual consumption behaviors similar to addiction, the symptoms are generally less severe when stopped abruptly. Therefore, while sugar has addictive qualities, it’s essential to recognize its nutritional role and manage intake wisely.
Can processed foods contribute to sugar addiction?
Yes, processed foods often contain high levels of added sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium, all of which increase palatability and may lead to increased consumption and cravings. This can create a cycle of habitual eating, making it challenging to reduce sugar intake. Being aware of these foods and their sugar content is crucial in addressing potential sugar addiction.
What strategies can help reduce sugar cravings?
To reduce sugar cravings, consider gradually decreasing sugar intake instead of eliminating it entirely. Focus on consuming whole foods, reading labels, and substituting sugary snacks with healthier options like fruits. Maintaining balanced meals and staying hydrated can also help mitigate cravings.
Is all sugar bad for you?
Not all sugar is bad for you. Naturally occurring sugars in fruits, vegetables, and dairy provide essential nutrients. The health concerns primarily arise from high intake of added sugars found in processed foods and sugary drinks. Moderation is key; while some sugar is necessary for dietary enjoyment and energy, excessive consumption can have negative health effects.
What role does sugar play in our diets?
Sugar can enhance flavor and texture in foods, making it pleasant to consume. While it’s beneficial to have some sweetness in our diets, the challenge lies in consuming it in moderation, particularly against the backdrop of an abundance of processed sugars available in our food supply. Being mindful of our sugar intake can help prevent health issues associated with excess consumption.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Cravings and Addiction | Sugar may cause cravings similar to addictive substances, but isn’t classified as addictive in clinical terms. |
| Comparison to Other Substances | Unlike alcohol and drugs, sugar is essential in moderation, found in fruits and other healthy foods. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Stopping sugar intake may cause mild withdrawal symptoms like headaches and anxiety. |
| Average Sugar Consumption | Average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, exceeding health recommendations. |
| Gradual Reduction is Key | It’s suggested to gradually reduce sugar intake rather than quitting abruptly to avoid adverse effects. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This is a widely debated question among nutrition experts. While sugar does elicit cravings and can lead to compulsive eating behaviors similar to those seen with addictive substances like alcohol and nicotine, it is not officially classified as an addictive substance. Moderation is essential, as excessive sugar intake can lead to health problems. Maintaining a balanced diet and being aware of added sugars can help mitigate negative effects while allowing us to enjoy the sweetness sugar brings to our lives.