In recent years, suicide prevention for older adults has become an increasingly urgent concern, particularly for those aged 75 and above who face significantly higher suicide rates than any other age group. Despite this alarming statistic, there remains a glaring deficit in accessible mental health resources for seniors that can adequately address their unique challenges. A study published in The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry reveals that many established suicide prevention organizations are not adequately reaching this vulnerable population, leaving them without the support they need. Social isolation, stigma, and underrepresentation in research all contribute to this crisis, emphasizing the need for targeted intervention and community support for elderly suicide risk. By fostering awareness and providing online suicide prevention resources tailored to older adults, we can help bridge this critical gap in mental health care and encourage those in need to seek help.
The issue of suicide among seniors, particularly those in their twilight years, highlights a pressing public health challenge that demands our immediate attention. Many elderly individuals experience feelings of loneliness, loss, and hopelessness, which can lead to an increased risk of self-harm. Although the conversation around mental health is growing, traditional support systems often fall short for older populations, necessitating a focused approach in geriatric psychiatry. Innovations in suicide prevention strategies for this demographic are essential, especially when considering the unique aspects of their mental health experiences. By creating avenues for assistance and providing comprehensive mental health resources for seniors, we can play a pivotal role in reducing the rates of suicide within this at-risk group.
Understanding Suicide Rates in Older Adults
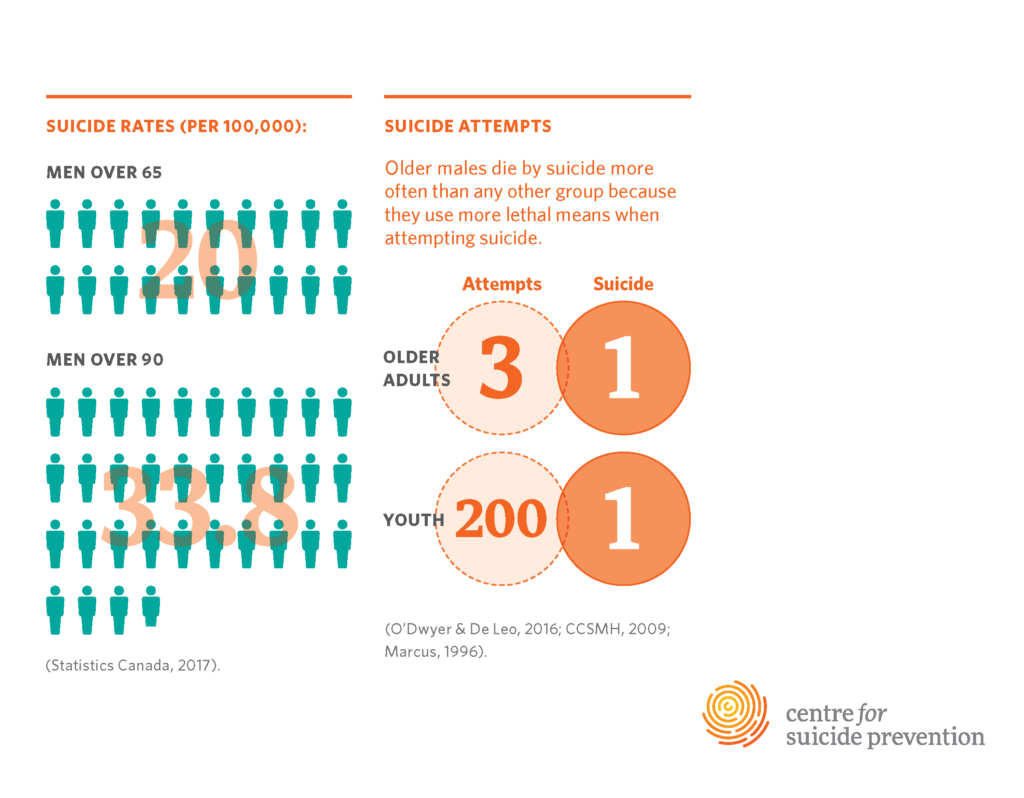
Suicide rates in older adults, particularly those aged 75 and above, have reached alarming levels, with statistics indicating that this demographic experiences one of the highest incidences of suicide at a rate of 20.3 per 100,000 people based on CDC data. The increasing prevalence of suicides among older adults stands in stark contrast to the declining rates observed in younger populations. This troubling trend can often be attributed to factors such as increasing social isolation, the complexity of mental health issues in late life, and the lack of adequate mental health resources tailored to the needs of older individuals.
The emphasis on understanding these rate dynamics is crucial as it not only elucidates why older adults are uniquely vulnerable, but it also highlights the inadequacy in current mental health programming. Many older individuals may struggle to voice their psychological distress, leading to a silent epidemic of mental health issues that contributes to the rising suicide rates. By raising awareness around geriatric mental health and identifying the factors at play, stakeholders can help create targeted interventions to support this at-risk population.
Mental Health Resources for Seniors: The Glaring Gap
Despite the high suicide rates amongst older adults, mental health resources specifically designed for seniors remain scarce. The research conducted by McLean Hospital underscores this concerning gap in resources, as older adults are often left without easy access to the information and support needed to address their mental health challenges. Many national suicide prevention organizations have not adequately embraced this demographic, leading to a detrimental consequence where the most vulnerable population does not receive the necessary intervention when needed.
To bridge this gap, various stakeholders—including healthcare providers, community organizations, and government agencies—must prioritize developing and promoting mental health resources tailored specifically for seniors. This could involve implementing training programs that emphasize geriatric psychiatry practices, while also ensuring that online resources are user-friendly. Creating awareness campaigns that resonate with older adults is crucial to reaching them effectively and ensuring they know where to turn for help.
Support for Elderly Suicide Risk: A Community Effort
Supporting elderly individuals at risk for suicide demands a community-wide effort, as the roots of suicide can often be traced back to broader societal issues, including social isolation and loneliness. Initiatives aimed at connecting older adults with community resources can help combat feelings of despair. Programs that encourage social engagement, physical activity, and intergenerational connections can create a support network that significantly lowers isolation rates—one of the primary contributors to suicidal ideation among the elderly.
Local support groups, educational workshops, and volunteer programs can provide crucial touchpoints that reinforce the message that help is available and that older adults are valued members of the community. By focusing on collective mental wellness and excellence in care, communities can not only reduce the immediate risks of suicide among older adults but also contribute to a cultural shift that prioritizes mental health at all ages.
The Role of Online Suicide Prevention Resources
In today’s digital age, online suicide prevention resources play a pivotal role in offering support to various age groups, including older adults. However, the existing online resources are often not tailored to meet the specific needs of seniors, many of whom may lack digital literacy or have unique mental health challenges that are not addressed by general content. This can lead to frustration and confusion, ultimately discouraging older adults from seeking help when they need it most.
Enhancing online suicide prevention resources to include simple navigation, age-appropriate language, and relatable content can significantly improve accessibility for older adults. Additionally, training family members and caregivers on how to effectively use these resources can empower them to assist their loved ones in crisis, ensuring that help is just a click away.
Geriatric Psychiatry: A Key Component in Suicide Prevention
As the field of geriatric psychiatry continues to evolve, it plays a critical role in addressing the mental health challenges faced by older adults, particularly those at risk of suicide. Specialists in this area are trained to recognize the intricacies involved in diagnosing and treating mental health issues in the elderly, where traditional approaches may fall short. A tailored and nuanced approach is crucial when assessing the mental health of older populations due to the unique life experiences and health-related limitations they face.
Furthermore, increasing awareness of the importance of geriatric psychiatry in suicide prevention can catalyze the development of specialized programs and resources that address the specific needs of older adults. These may include psychotherapy tailored to seniors, medication management, and the integration of physical health into mental health discussions, emphasizing a holistic approach to well-being.
Creating Targeted Campaigns for Older Adults
To effectively combat the rising suicide rates among older adults, it is crucial to develop targeted outreach campaigns specifically aimed at this demographic. Such campaigns should not only raise awareness about mental health issues but also provide vital information on available resources and support systems. Highlighting testimonials from older adults who have sought help can serve as powerful narratives that resonate with peers, potentially encouraging them to reach out and seek the help they need.
Incorporating input from older adults in the creation of these campaigns ensures that the messaging is relatable and meaningful. Engaging community leaders and healthcare professionals in these discussions can provide valuable insights, leading to campaigns that are both effective and sensitive to the unique needs of older citizens.
The Importance of Funding in Geriatric Mental Health
Increased funding for geriatric mental health initiatives is vital to addressing the suicide crisis among older adults. Without adequate financial resources, programs designed to provide targeted interventions and support become limited, ultimately hindering their effectiveness. Investment in research, community health programs, and educational initiatives focused on late-life suicide prevention can result in substantial changes that save lives.
Additionally, securing funding for training programs in geriatric psychiatry will empower healthcare providers with the skills needed to identify and respond to older patients’ mental health crises effectively. When communities prioritize mental health funding, they send a clear message about the importance of caring for their older citizens, reinforcing that no one is forgotten or left behind.
Navigating Mental Health in Later Life
Navigating mental health in later life presents unique challenges that can often be overwhelming for older adults. Changes in health, loss of loved ones, and diminishing social circles can significantly impact mental well-being, heightening the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts. It’s essential to provide comprehensive mental health resources that cater to these changing realities and offer clear pathways for obtaining help.
Empowering older adults through mental health education and awareness campaigns can facilitate better understanding and utilization of available resources. Whether through community programs, support groups, or virtual platforms, creating multiple access points ensures that older adults can find the help they need when they need it.
Building a Future of Supportive Resources for Seniors
The future of suicide prevention for older adults hinges on the development of more supportive resources and the effective dissemination of information tailored to their needs. Emphasizing the importance of community and healthcare provider involvement in creating sustainable programs can result in long-term positive outcomes for older adults. These initiatives could include intergenerational support systems, virtual counseling services, and comprehensive training for all caregivers.
By establishing a robust network of support, we can create an environment in which older adults feel safe discussing their mental health concerns and understand that resources are available. Cultivating a sense of belonging and inclusion is paramount in addressing the mental health crisis in later life, ultimately contributing to the prevention of suicide among this vulnerable population.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the suicide rates in older adults compared to other age groups?
Older adults, especially those aged 75 and older, have the highest suicide rates of any age group, estimated at 20.3 per 100,000 according to the CDC. This rate has been increasing, unlike younger populations where rates have declined.
What mental health resources for seniors are available to prevent suicide?
While resources specifically targeting older adults are limited, seeking support through community health organizations, senior centers, and geriatric psychiatry experts can provide valuable mental health resources for seniors at risk of suicide.
How does geriatric psychiatry address suicide prevention for older adults?
Geriatric psychiatry focuses on the mental health needs of older adults, employing tailored therapeutic approaches and crisis intervention strategies to effectively address and prevent suicides in this vulnerable population.
What support for elderly suicide risk can family members provide?
Family members can play a vital role in suicide prevention for older adults by providing emotional support, encouraging open conversations about mental health, and helping them access professional mental health resources and services.
Are there online suicide prevention resources specifically for older adults?
Although online resources for older adults are scarce, initiatives are underway to develop tailored online suicide prevention resources, targeting the unique needs and barriers faced by the elderly demographic.
How can communities improve suicide prevention efforts for older adults?
Communities can enhance suicide prevention efforts for older adults by creating targeted campaigns, increasing awareness of available mental health resources, and promoting social engagement to combat isolation.
What role does social isolation play in the suicide rates of older adults?
Social isolation significantly contributes to the high suicide rates among older adults, as it often leads to loneliness and mental health deterioration. Promoting social connections is essential in mitigating this risk.
Why is there a lack of resources for suicide prevention in older adults?
The shortage of resources for suicide prevention in older adults may stem from underrepresentation in research, systemic biases, and a general lack of awareness about the specific needs of this age group.
What steps can be taken to create more accessible suicide prevention resources for older adults?
To create more accessible suicide prevention resources for older adults, it is critical to conduct research on their needs, increase funding for tailored programs, and ensure that online resources are user-friendly and easy to find.
How can older adults access mental health services for suicide prevention?
Older adults can access mental health services for suicide prevention through their healthcare providers, local mental health organizations, or hotlines that offer immediate assistance and referrals to specialized care.
| Key Topics | Details |
|---|---|
| Highest Risk Group | Older adults, especially those aged 75 and older, have the highest suicide rates of any age group. |
| Lack of Resources | Study shows that suicide prevention organizations provide few resources tailored to older adults. |
| Study Findings | Research from McLean Hospital highlights the imbalance in online suicide prevention targeting younger populations over older adults. |
| Suicide Rate | Adults aged 75+ have a suicide rate of 20.3 per 100,000, which is increasing compared to other age groups. |
| Social Factors | Social isolation and loneliness are significant contributors to the higher suicide rates among older adults. |
| Call to Action | There is a need for targeted suicide prevention campaigns that address the unique needs of older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent issue that requires focused attention and action. Given that older adults are at a higher risk of suicide, especially those over the age of 75, it’s crucial to enhance the availability of resources specifically designed for them. Despite the known vulnerability of this demographic, current online suicide prevention resources fall short in addressing their unique healthcare needs. Efforts must be made to develop targeted campaigns and accessible online platforms to reach and support older adults effectively. Furthermore, more funding and research on late-life suicide prevention will be essential to improve the situation and reduce these alarming rates.